http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/chemical/bond.html
http://www.visionlearning.com/en/library/Chemistry/1/Chemical-Bonding/55
http://www.chem1.com/acad/webtext/chembond/
http://www.chem4kids.com/files/atom_bonds.html
http://www.chem4kids.com/
http://www.acs.org/content/acs/en.html
http://www.rsc.org/
http://chemistry.about.com/
https://chemistry.stanford.edu/
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/03088146
http://www.nature.com/nchem/index.html
http://scienceworld.wolfram.com/chemistry/
http://chemistry.bd.psu.edu/jircitano/gases.html
http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch4/gaslaws3.html
http://antoine.frostburg.edu/chem/senese/101/gases/
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/gases-and-kinetic-molecular-theory/ideal-gas-laws/v/ideal-gas-equation-pv-nrt
Tuesday, May 10, 2016
Bonding 3
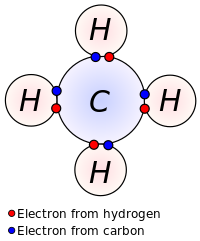
In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.
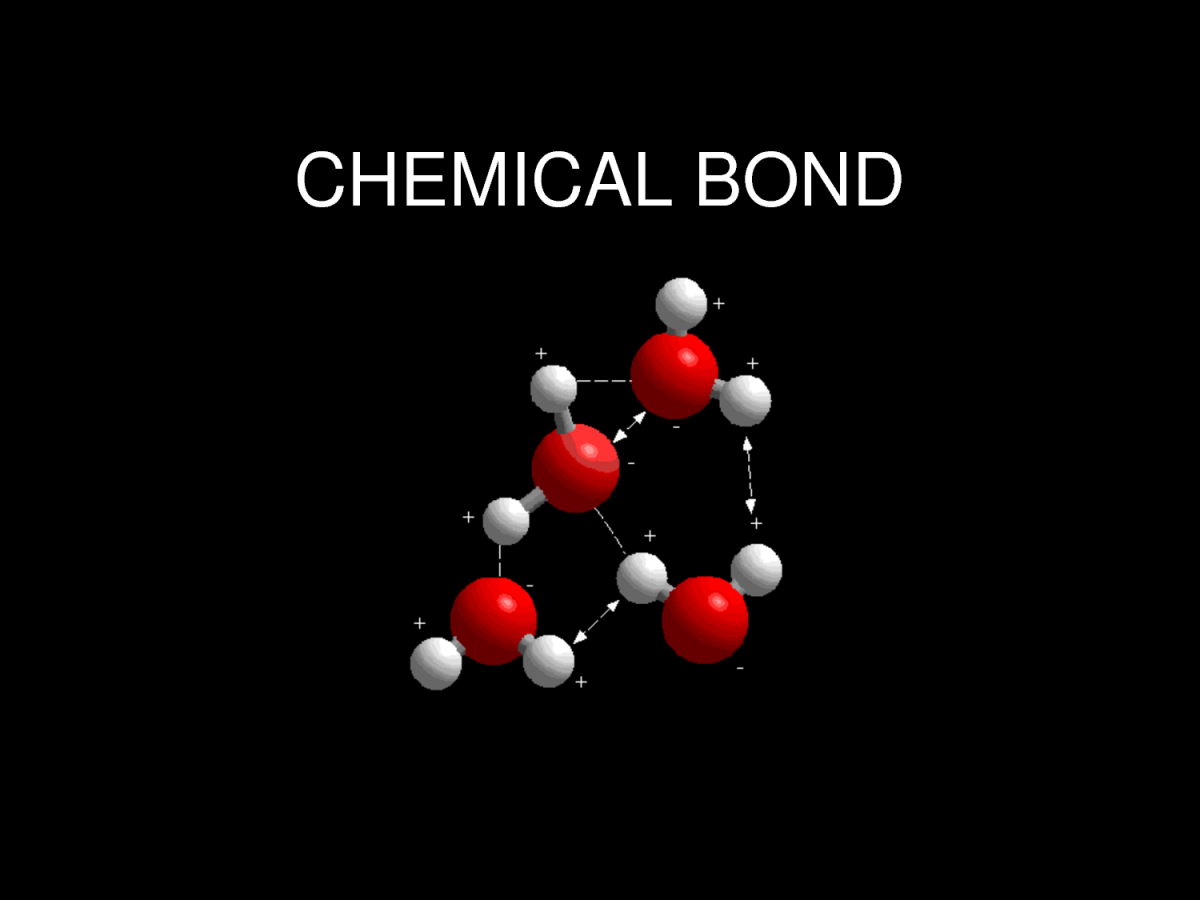

Bonding 2
Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.

Bonds 1
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms that enables the formation of chemical compounds. The bond may result from the electrostatic force of attraction between atoms with opposite charges, or through the sharing of electrons as in the covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" such as covalent or ionic bonds and "weak bonds" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.

Monday, May 9, 2016
Energy and phase changes 2
The unit most associated with energy is joules, but we can use the unit calorie when we are taking about the amount of energy to raise the temperature of one gram of substance by 1C.
Intermolecular-occurs between molecules.
Intramolecular-occurs within a molecule.
Energy and phase changes
Chemical reactions involve not just the conversion of reactants into products, but also involve an energy change in the form of heat. Heat released as the result of a reaction, or heat abosorbed as a reaction proceeds. Energy changes happen when the chemical bonds are moved around.
There are four types of energy. 1)radiant energy: energy from the sun or solar energy. 2)thermal energy: energy associated with the random motion of atoms. 3)chemical energy: energy stored within the structural units of chemical substances. 4) potential energy: energy stored in the composition of a substance.
Thursday, May 5, 2016
Biodiesel 3
The main ingredient in biodiesel is methanol. Biodiesel is commonly produced by the transesterification of the vegetable oil or animal fat feedstock. There are several methods for carrying out this transesterification reaction including the common batch process, supercritical processes, ultrasonic methods, and even microwave methods.
Biodiesel 2
Biodiesel is meant to be used in standard diesel engines and is thus distinct from the vegetable and waste oils used to fuel converted diesel engines. Biodiesel can be used alone, or blended with petrodiesel in any proportions.
Biodiesel 1
Biodiesel is a clean source of energy that should be used more often. It releases less harmful chemicals than other forms of fuel and is also renewable. We get it from breaking down used vegetable oil and processing it into a usable form of energy.
Tuesday, May 3, 2016
Charles' Law
Charles' Law tells us that temperature and volume vary directly with each other as long as the pressure is constant. This does not apply for absolute zero, which is a theoretical temperature in which all movement stops. Including the movment of electrons.
Kelvin
The temperature for all Charles' Law problems must be done in kalvin. The Kelvin scale is an absolute scale. The conversion for kalvin is: C+273.15
Gas law 2
Boyle's Law uses pressure and volume to find out curtain aspects about a gas. It tells us that the realationship between pressure and volume is an inverse relationship. This holds true at a constant temperature.
Gas law 1
Gases form homogeneous mixtures. Also they are highly compressible and fill what ever they are in. The collisions that take place between the molecules are elastic. A barometer is commonly used to measure atmospheric pressure.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)









